Office Hours
Mon - Fri: 8:00 am - 5:00 pm Closed on Weekends
Toll Free
1-800-850-3440
Locations
Youngstown, OH, Cleveland, OH & Pittsburgh, PA
Office Hours
Mon - Fri: 8:00 am - 5:00 pm Closed on Weekends
Toll Free
1-800-850-3440
Locations
Youngstown, OH, Cleveland, OH & Pittsburgh, PA
Air compressors are vital in a wide range of industries, powering equipment, tools, and processes. Depending on the application, compressors vary in design, functionality, and capacity. There are several types of compressors available, each offering unique benefits tailored to specific needs. In this blog, we will explore different types of air compressors, including oil-lubricated, oil-free, and special application compressors, and their advantages. Whether you’re looking for a solution for heavy industrial use or lighter applications, there’s a compressor to fit your needs.
Oil-lubricated compressors use oil to lubricate moving parts, such as pistons or rotors, during operation. The oil helps reduce friction, cools the components, and improves overall efficiency by extending the lifespan of the compressor. These compressors are widely used in industrial and commercial settings where high volumes of compressed air are required, as the oil provides smoother operation and better durability compared to oil-free models. While oil-lubricated compressors are not suitable for applications requiring oil-free air, their reliability and ability to handle heavy-duty tasks make them ideal for industries like manufacturing, automotive, and construction.
Fixed-speed oil-lubricated compressors operate at a constant speed, regardless of the air demand. They are typically used for applications that require a steady flow of compressed air.
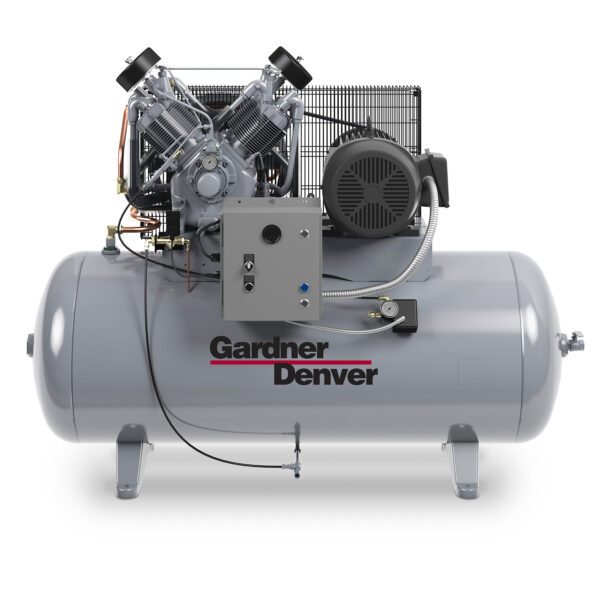

Reciprocating compressors are one of the oldest and most common types of fixed-speed compressors. They use a piston and cylinder mechanism to compress air and store it for later use. Reciprocating compressors are known for their high efficiency, compact design, and reliability, making them ideal for small to medium-sized industrial applications. Their ability to handle both small and large air volumes, makes them great for applications where moderate to high air demand is required.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
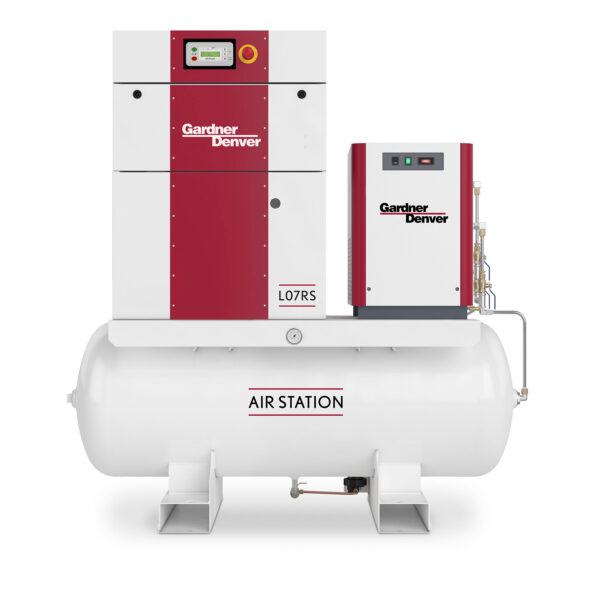

Air rotary stations are integrated systems that use rotary compressors to provide a continuous supply of compressed air for various industrial applications. These stations typically combine the rotary compressor, air dryers, filters, and air tanks into one cohesive unit, making them efficient and easy to maintain. Air rotary stations are known for their efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle large volumes of compressed air with minimal energy consumption. They are commonly used in industries where a constant, uninterrupted air supply is essential.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
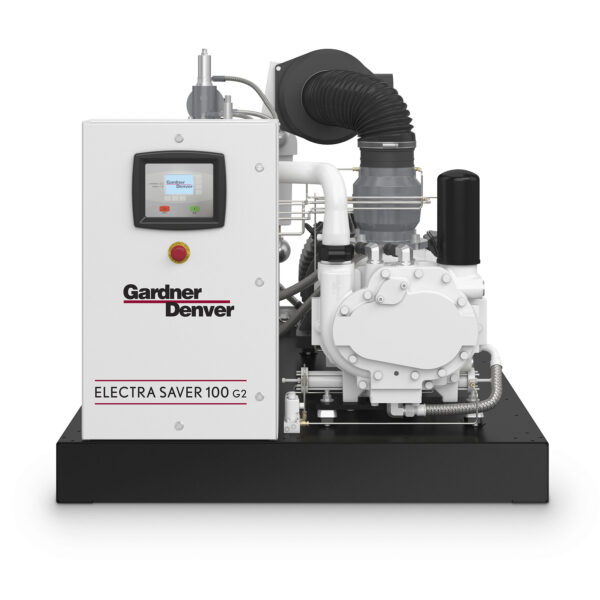

Rotary compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that use a rotating mechanism, typically in the form of helical rotors or vanes, to compress air. These compressors provide continuous, smooth airflow and are known for their efficiency, durability, and quieter operation compared to reciprocating compressors. Rotary compressors are ideal for applications that require consistent air supply, particularly in industrial environments. They are capable of handling high volumes of air with minimal pulsation and are commonly used in both small-scale and large-scale operations.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
Variable capacity oil-lubricated compressors adjust their speed and output based on the air demand, providing greater energy efficiency. These systems are perfect for applications where air demand fluctuates, as they optimize energy consumption.
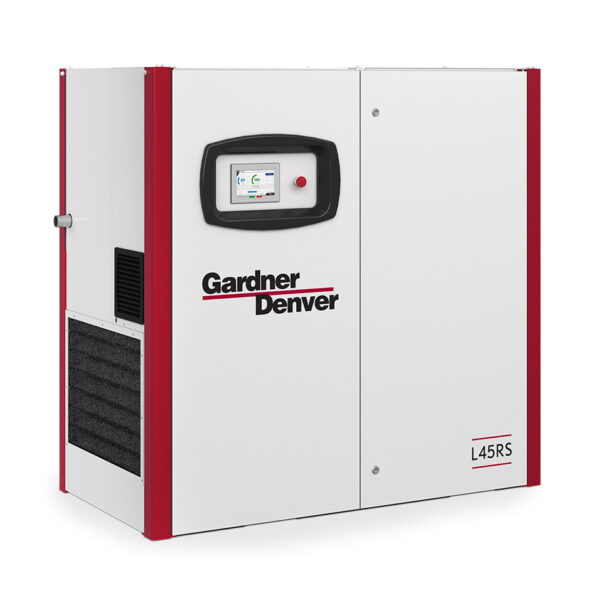

Rotary single-stage variable speed compressors use a single set of rotors to compress air. The variable speed control allows the compressor to operate at varying speeds, optimizing energy consumption and maintaining a consistent air supply. These systems automatically adjust their motor speed to match the demand for compressed air. This type of compressor is ideal for industrial applications where air demand changes frequently.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
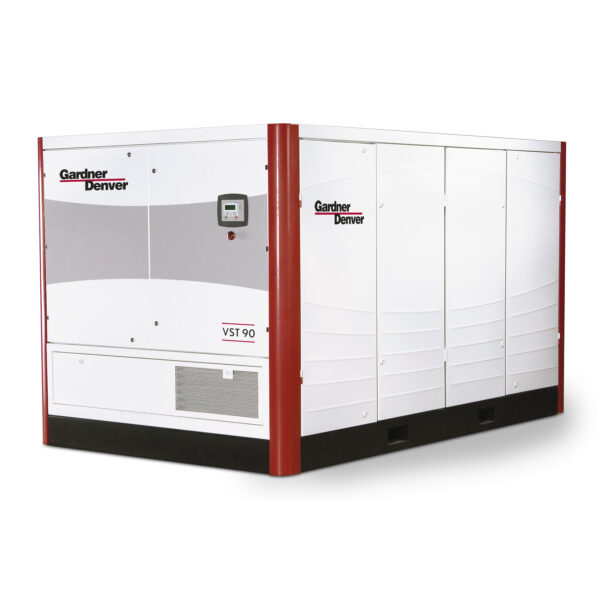

Rotary two-stage variable speed compressors have two stages of compression (intermediate and final), which allows for higher pressure ratios and more efficient air delivery. This design provides smoother performance and reduces the strain on the system. It’s particularly useful for high-demand applications where both efficiency and reliability are critical.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
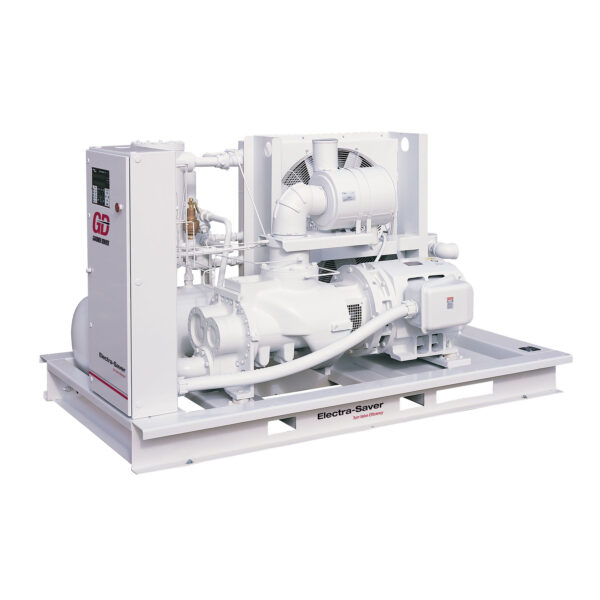

Rotary variable capacity compressors feature advanced control systems that adjust the system’s output to match varying levels of air demand. These systems can modulate their capacity to only meet current requirements. This technology allows for precise management of energy use, providing both flexibility and savings.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
Oil-free compressors are designed without the need for oil lubrication, making them ideal for applications where even the smallest trace of oil contamination would be harmful. These compressors are more expensive but are perfect for industries with strict air quality standards.
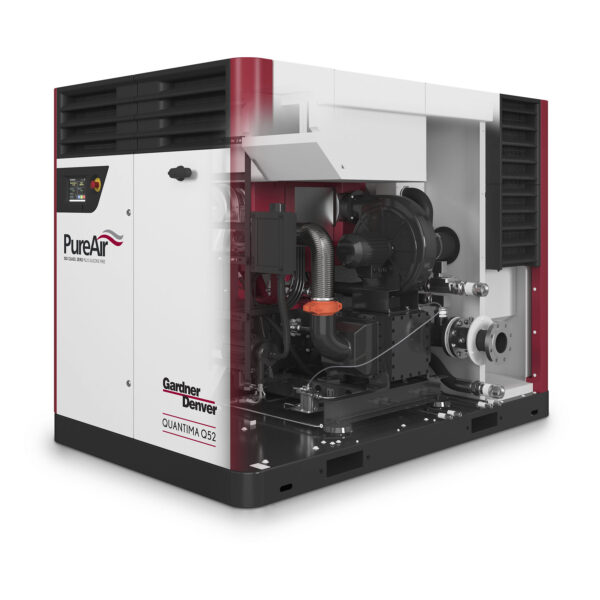

Centrifugal compressors use high-speed rotating impellers to compress air. Centrifugal compressors are widely used in various industries where high-volume, high-pressure gas flow is required, such as in natural gas processing, and air compression for manufacturing processes.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
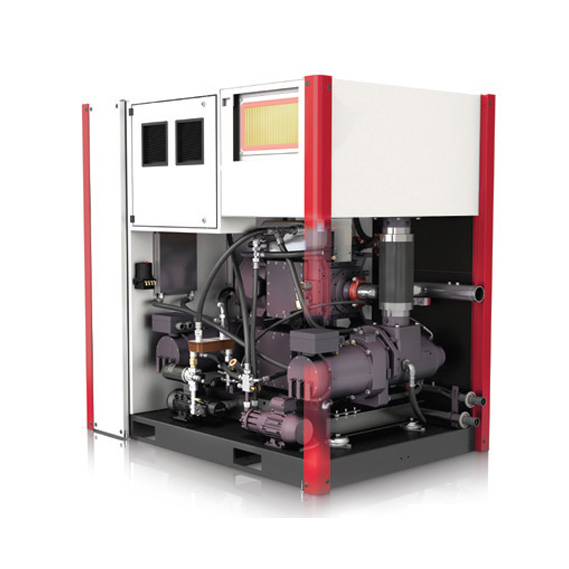

Rotary screw oil-free compressors operate using two interlocking helical screws that rotate to trap and compress air, maintaining a consistent continuous flow. Since these compressors do not use oil in the compression process, they are ideal for applications that require clean, oil-free air, preventing any contamination of the compressed air with oil particles. These compressors are commonly used in industries where purity of air is critical.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
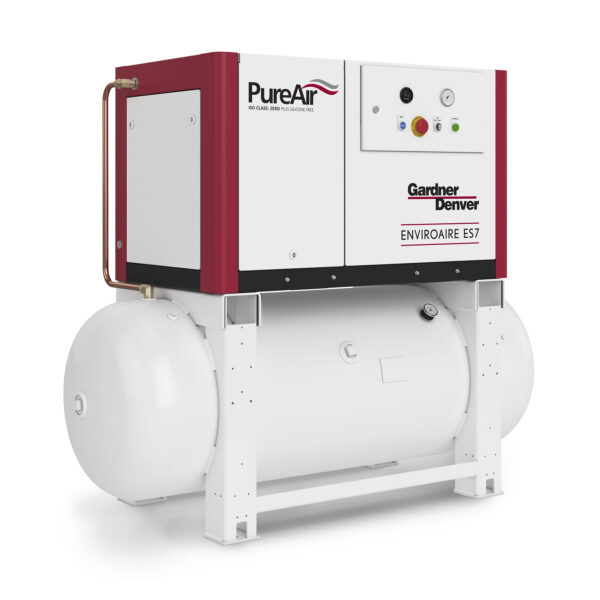

Scroll compressors are one of the most efficient oil-free technologies available. These compressors use two interlocking spiral scrolls to compress the air, providing quiet and efficient operation. They are ideal for smaller applications but can be scaled up for larger uses as well.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
In certain industries, specialized compressors are required to meet unique operational needs. These compressors are engineered to handle extreme conditions, such as high pressure or large air volumes.

Special application high-pressure compressors are designed to generate compressed air or gas at significantly higher pressures than standard compressors. These compressors typically operate at pressures ranging from 150 psi to several thousand psi, depending on the specific application. These compressors are built to withstand higher operational stresses and are equipped with safety features to handle the extreme pressures involved, making them vital for industries where high-pressure gas storage, delivery, or testing is required.
Key Features:
Best Suited Industries:
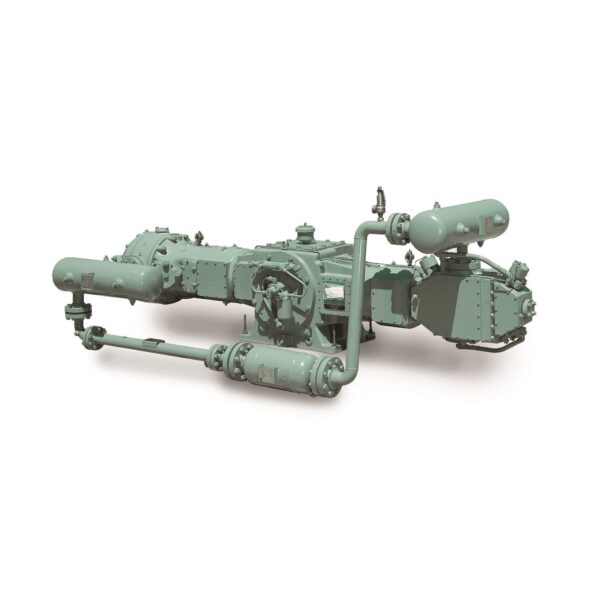
Special application large reciprocating compressors are robust machines designed to handle high-volume, high-pressure gas compression, typically used in demanding industrial applications. These compressors use a piston-driven mechanism to compress gas in cylinders, with the reciprocating motion of the piston creating pressure within each chamber. These compressors are often custom-built to meet the specific needs of high-demand industries, offering reliable performance in environments that require consistent, heavy-duty gas compression.
Key Features:
Best Suited Industries:
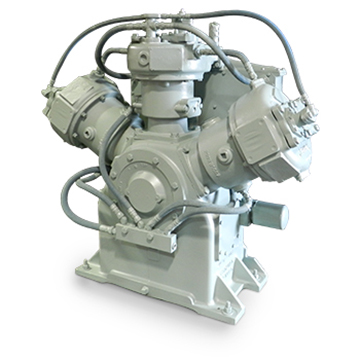
Special application locomotive compressors are designed specifically for railway systems, providing compressed air to power critical functions on trains, such as braking systems, horn operation, and door mechanisms. These compressors are typically heavy-duty and capable of withstanding the rigors of continuous use in harsh environments, including temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and exposure to dust and moisture. They are engineered to deliver reliable, high-performance compression to ensure safe and efficient train operations. These compressors are often mounted on the locomotive and work in conjunction with other systems to ensure optimal functioning across various operational conditions.
Key Features:
Best Suited For:
Selecting the right air compressor is crucial for ensuring efficient operations across various industries. With a broad range of compressor types—from oil-lubricated and oil-free compressors to specialized models like high-pressure and rotary systems—each offers distinct advantages tailored to specific applications. Understanding the unique needs of your industry, whether it be manufacturing, automotive, food processing, or pharmaceuticals, is key to choosing the right compressor for optimal performance, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully considering factors such as air demand, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions, businesses can make informed decisions that support long-term reliability and productivity.
Contact us today to see what type of compressor will suit your situation best!
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Toll Free: 1-800-850-3440
Email: info@dearingcomp.com
Copyright © Dearing Compressor & Pump Co. 2024 — All rights reserved. | Privacy Policy | Site Created By 898 Marketing
Mon - Fri: 8:00 am - 5:00 pm
Closed on Weekends
Toll Free
1-800-850-3440
Youngstown, OH, Cleveland OH, & Pittsburgh, OH